Recently, the team led by Professors Zhao Chan and Chen Youxin from the Department of Ophthalmology, PUMCH, in collaboration with Zhang Yanchun’s team from Shanxi Provincial Eye Hospital, validated the efficacy prediction role of a high-performance aqueous vascular endothelial growth factor (VEGF) detection system in macular edema secondary to retinal vein occlusion (RVO-ME), a common blinding eye disease. Their paper won the Best Scientific Paper Presentation at the 39th Asia-Pacific Academy of Ophthalmology (APAO) Congress. It was the only award-winning paper in the field of translational medicine at this congress.

Retinal vein occlusion (RVO) is one of the most common retinal vascular diseases, more prevalent among populations with hypertension and hyperlipidemia. It often causes macular edema, even blindness in severe cases. Currently, anti-VEGF therapy is the first-line treatment for RVO-ME, but a significant portion of patients respond poorly to anti-VEGF drugs or gradually lose sensitivity during treatment.
Currently, clinicians can only determine treatment effectiveness after multiple rounds of therapy, as there is no reliable method of efficacy prediction. If the treatment turns out to be ineffective, it not only delays proper care and potentially affects prognosis, but also wastes valuable medical resources. Just when researchers puzzled over how to achieve more accurate efficacy prediction for RVO-ME, “companion diagnostics” drew their attention. It’s an in vitro diagnostic technique that provides information on patients’ response to specific drugs.
Inspired by this, Zhao Chan’s team introduced the concept of companion diagnostics to ophthalmological diseases for the first time, which was published as a review in an international academic journal in 2022. The team also developed a high-performance aqueous humor VEGF detection system, comprising a magnetic particle chemiluminescence micro aqueous humor VEGF detection kit and a fully automated analyzer. Used in combination with the world’s first aqueous humor collection device developed and approved for marketing by the team earlier, the detection system can achieve real-time testing of aqueous humor VEGF. The automatic system is able to provide results in 45 minutes with only 20 μL sample, with high accuracy, sensitivity, and reproducibility. These virtues make it a pioneering ophthalmological diagnostic method.
Based on this, the team studied the predictive effect of imaging parameters and aqueous humor VEGF on the efficacy of one single anti-VEGF treatment in RVO-ME patients. The study found that baseline central macular thickness and aqueous humor VEGF concentration are independent predictors of anti-VEGF treatment for RVO-ME. Combining the two to construct an efficacy prediction model can further improve prediction accuracy. This study preliminarily verified the feasibility of companion diagnostics based on aqueous humor VEGF detection for RVO-ME, potentially pioneering a new treatment paradigm based on companion diagnostics of intraocular fluid.
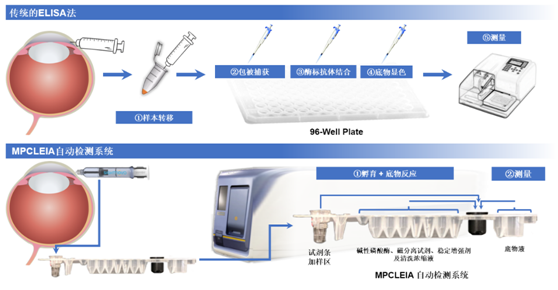
▲Comparison of aqueous humor VEGF concentration detection using the traditional ELISA method and the high-performance VEGF detection system developed by the team
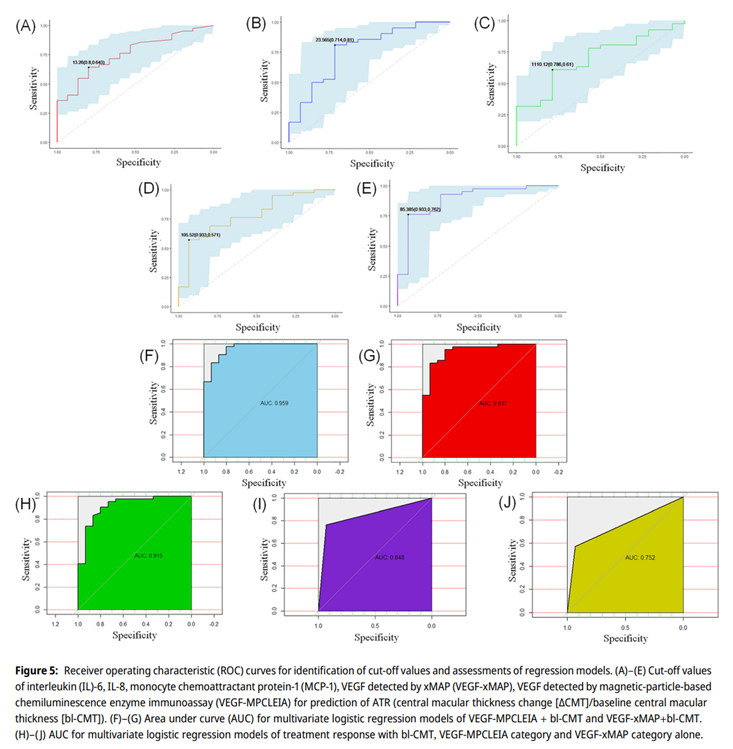
▲Receiver operating characteristic (ROC) curves for identification of cut-off values and assessment of regression models. (A)-(E) Cut-off values of interleukin (IL)-6, IL-8, monocyte chemoattractant protein-1(MCP-1), VEGF detected by xMAP (VEGF-xMAP), VEGF detected by magnetic-particle-based chemiluminescence enzyme immunoassay (VEGF-MPCLEIA) for prediction of ATR (anatomical treatment response)
Pictures courtesy of the Department of Ophthalmology
Edited by Wang Jingxia
