The team of Prof. Jiang Yuxin and Prof. Yang Meng from the Department of Diagnostic Ultrasound, PUMCH, in collaboration with Prof. Wang Qian, Prof. Li Mengtao and Prof. Zeng Xiaofeng from the Department of Rheumatology, carried out the first cohort study globally that applied multimodal photoacoustic/ultrasound (PA/US) imaging to quantitatively assess the oxygen saturation (SO2) of synovial tissues in patients with rheumatoid arthritis (RA) and evaluate their disease activity. The research results were recently published in Radiology (IF: 29.146), a top international journal in radiology. Significance of the study lies in providing a new strategy for accurate assessment of disease activity in inflammatory arthropathy, and a new technique and a new method for studying the mechanism of tissue oxygenation correlation with diseases and its application in clinical diagnosis and treatment. This study has visibly boosted the international influence of China’s research on the clinical translation of photoacoustic imaging.

Accurate assessment of disease activity is the key to the “treat-to-target” of RA. The common approach for that is a clinical index-based scoring system, which is somewhat subjective. Ultrasound is an important assisting imaging method for RA diagnosis and treatment, providing a basis and additional information for clinical assessment, but the results of previous relevant studies were controversial. Given these drawbacks, a new imaging tool is needed to complement ultrasound imaging and provide additional information for diagnosis.
Tissue hypoxia triggers the activation and proliferation of aberrant immune cells and exacerbates the inflammatory response through complex signaling pathways, which is also a therapeutic target for RA. Therefore, identifying hypoxia may be helpful to RA diagnosis and treatment. Multimodal PA/US imaging combines the advantages of PA and US, thereby able to provide information on tissue structure and also obtain local tissue oxygen saturation by measuring deoxyhemoglobin and oxygenated hemoglobin levels. Thus, multimodal PA/US imaging can help assess the local synovial tissue oxygenation status in RA patients.
This study was a prospective observational cohort study that consecutively enrolled 118 RA patients who attended the outpatient rheumatology clinic of PUMCH from 2019 to 2021 and recruited 15 healthy volunteers as controls. Clinical and laboratory tests were performed to assess disease activity, and multimodal PA/US imaging was performed on RA patients and healthy volunteers. Tissue SO2 values were measured, and RA patients were grouped based on the oxygenation status. Then the correlation between semi-quantitative scores in power-Doppler US (PDUS) and disease activity was analyzed and compared among different groups.
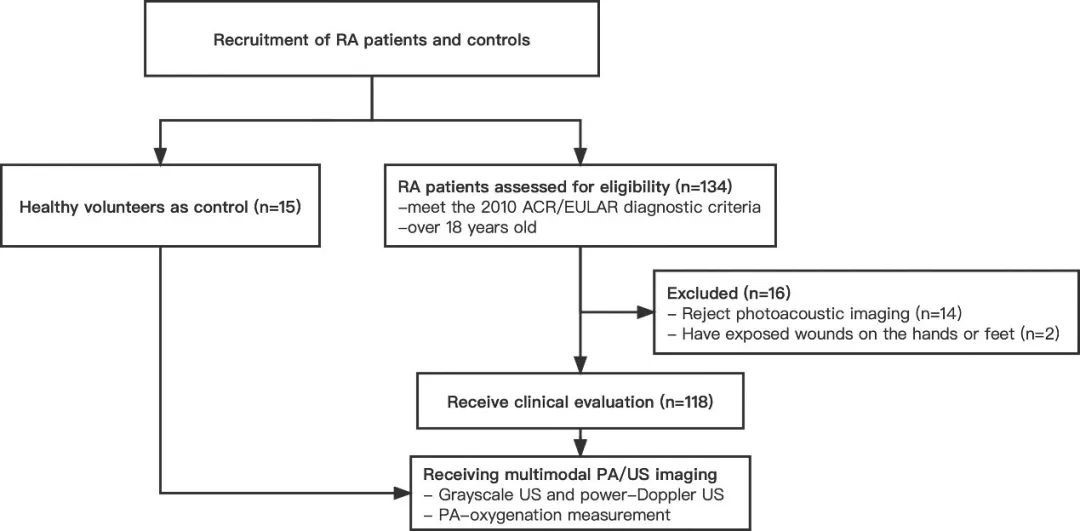
▲Flowchart of the patient enrollment process
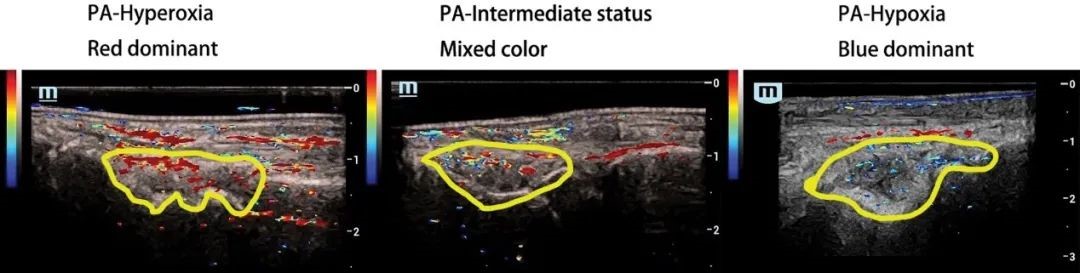
▲Three groups with different synovium oxygenation status based on PA imaging
According to study results, the PA- SO2 values ranged from 88% to 96% for healthy volunteers in the normal tissues around the wrist synovial tissue, and ranged from 58% to 95% for RA patients in the wrist synovial tissue. Synovial tissue oxygenation status correlated with PDUS vascularization. Hyperoxic synovium had more affluent PDUS-depicted vasculature than those with hypoxia, while the group with intermediate oxygenation status had lower clinical scores and more patients in clinical remission than the hypoxia group.
Conventional wisdom holds that low PDUS-depicted vascularity is associated with low disease activity. However, this study found that the hypoxic synovium was correlated with higher disease activity, although it tended to be associated with low vascularity. This indicates the complementary role that PA imaging of tissue oxygen saturation can play in the ultrasound assessment of RA. Multimodal PA/US imaging holds the potential for optimizing and enhancing the efficacy of conventional ultrasound in accurately assessing disease activity in patients with RA and informing the development of treatment strategies.
Translated by Liu Haiyan
Edited by Zhang Li and Wang Yao
