A growing body of research suggests that biological clocks not only regulate the timing of bodily processes, but also are closely related to metabolic health and the risk of chronic disease. The team of Mao Yilei and Yang Huayu from the Department of Liver Surgery at PUMCH compared the effects of different eating patterns, one being three normal meals a day and the other two time-restricted eating patterns, on the health status of healthy adults; the study found out that “morning meal” can improve fasting blood sugar, reduce body weight and body fat, improve inflammation levels, increase gut microbial diversity, and be more effective in improving insulin sensitivity and controlling blood sugar. The research results were published online on February 22, 2022 in “Nature Communications”, a sub- journal of “Nature”.

The team of Mao Yilei and Yang Huayu published a research paper titled “Randomized controlled trial for time-restricted eating in healthy volunteers without obesity”
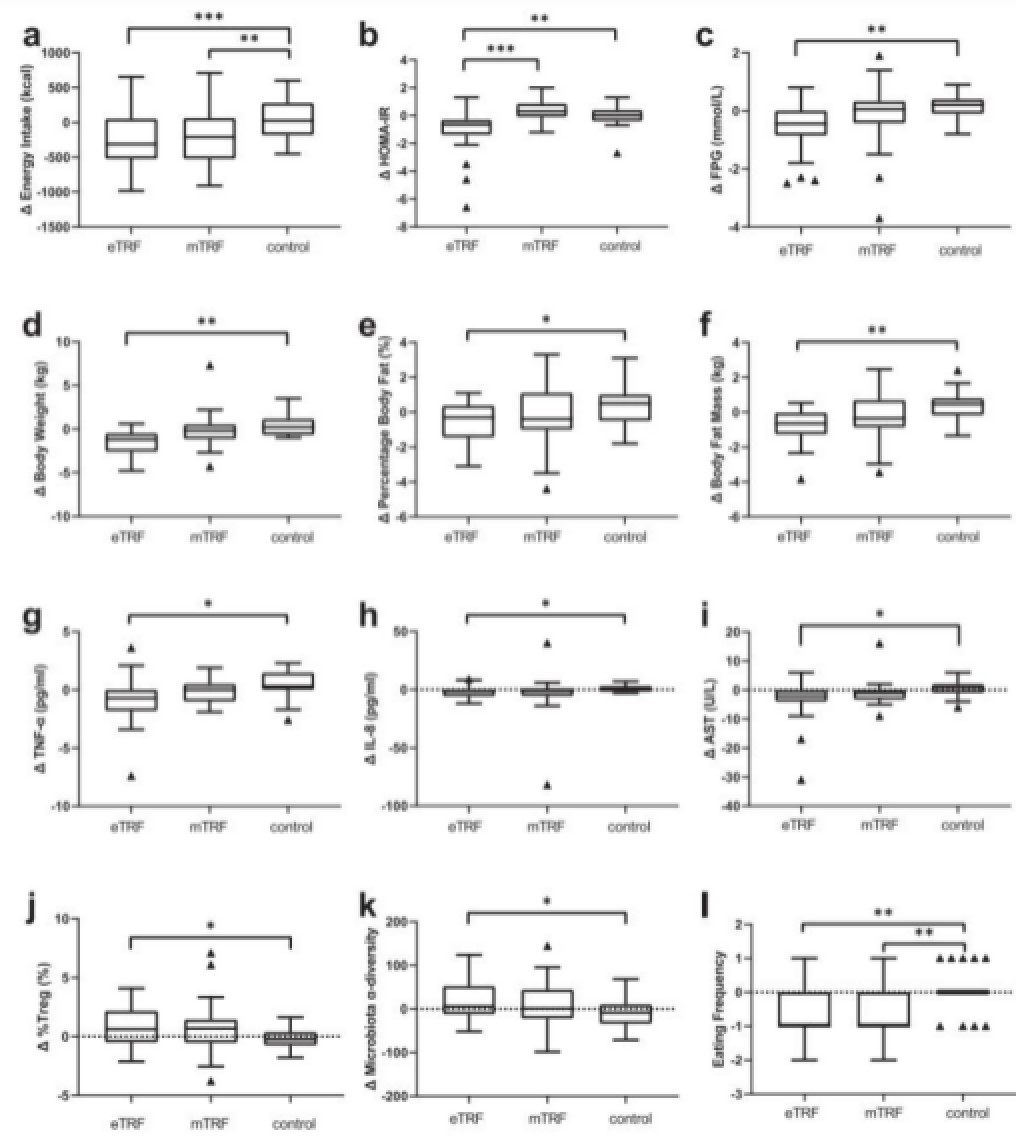
Energy intake and metabolic health-related statistics of volunteers in the 3 groups
Reporter: Gan Dingzhu
Picture: The Department of Liver Surgery
Translator: Liu Haiyan
Editor: Xu Haifeng and Wang Yao
