Recently, a multidisciplinary team led by Li Yongzhe, researcher in the Department of Clinical Laboratory; Xu Tengda, chief physician in the Department of Health Management; and Wang Li, chief physician in the Department of Rheumatology at PUMCH conducted a retrospective cohort study to identify predictive biomarkers for primary biliary cholangitis (PBC) development in anti-mitochondrial antibody M2-positive (AMA-M2) individuals. The team developed a risk prediction model for PBC progression in this population. The findings were published in Clinical and Molecular Hepatology (IF=14), a journal ranked among the top 5% by the Chinese Academy of Sciences. This research was supported by the National Key R&D Program and National High-Level Hospital Clinical Research Funding.

AMA-M2 is a specific marker for PBC and it could also be present in healthy individuals without PBC and patients with other conditions. The predictive value of AMA-M2 for future PBC development in non-PBC populations remains unclear.
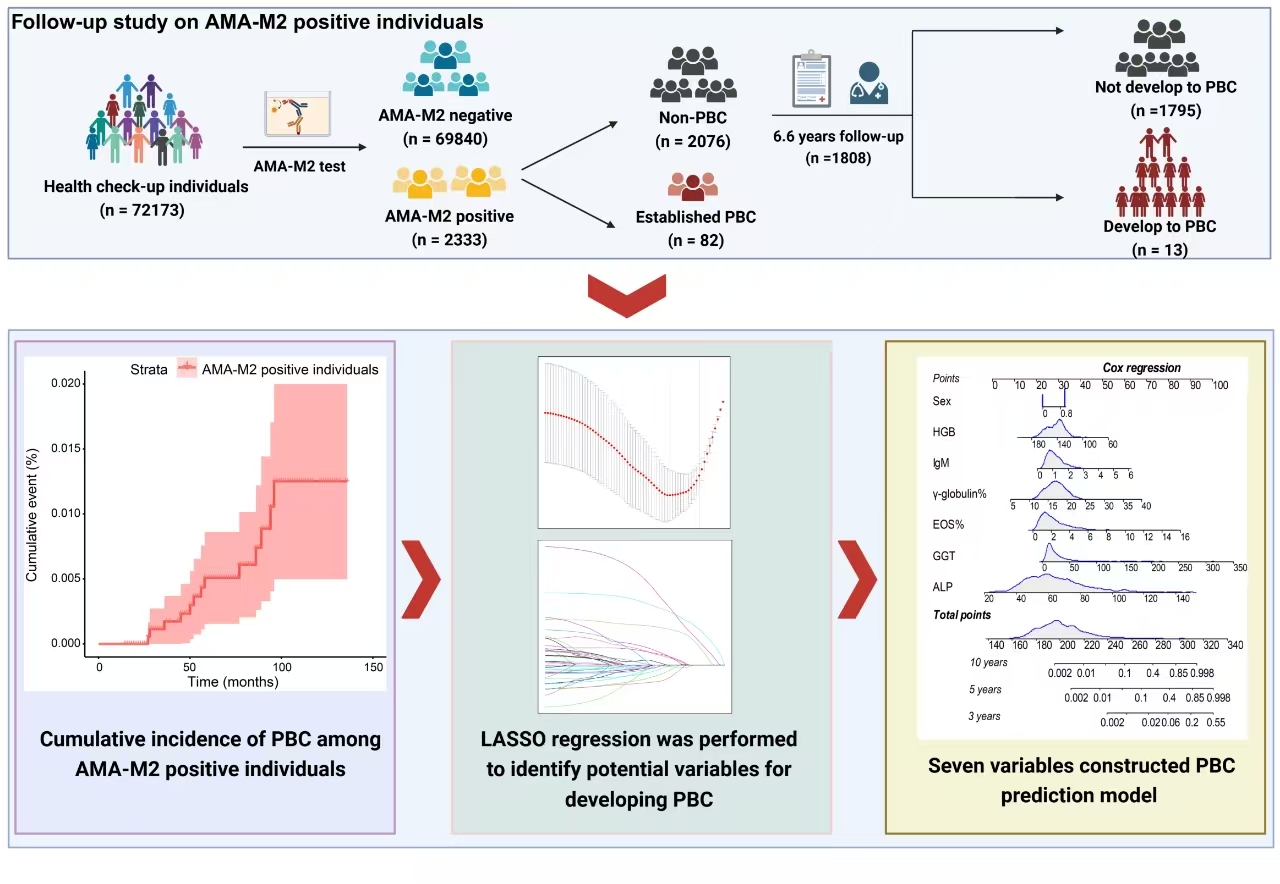
The research team conducted a retrospective cohort analysis of 72,173 individuals who underwent health check-ups at PUMCH's Department of Health Management between 2010 and 2022, determining the prevalence of AMA-M2 positivity. The team then followed up with individuals who tested AMA-M2-positive at baseline but had not yet developed PBC, tracking their progression to PBC. The researchers integrated baseline data from the AMA-M2-positive non-PBC population to identify and validate early abnormal variables significantly associated with PBC development.
▲Graphical abstracts
The analysis identified 2,333 individuals positive with AMA-M2, indicating a prevalence of 3.23%. Of these, 82 individuals had a medical history of PBC. Among the AMA-M2-positive individuals without PBC at baseline, 13 developed PBC during follow-up, representing an incidence rate of approximately 98 per 100,000 persons per year—substantially higher than previously reported PBC incidence rates in the general population (0.03-0.58 per 100,000 persons per year).
Regression analysis identified potential predictors closely associated with PBC development in this population: alkaline phosphatase (ALP), gamma-glutamyl transpeptidase (GGT), immunoglobulin M (IgM), eosinophilia proportion (EOS%), gamma globulin percentage, and hemoglobin (HGB). A predictive model incorporating these biomarkers demonstrated robust predictive value for identifying future PBC occurrence among AMA-M2-positive individuals.
By innovatively utilizing health check-up data, this study establishes a novel data source for future research, unlocking the potential value of general population data. By identifying predictive biomarkers and constructing a validated risk prediction model, the research provides evidence-based guidance for early identification of high-risk PBC populations.
Researcher Li Yongzhe, Chief Physicians Xu Tengda and Wang Li are co-corresponding authors. Li Haolong (technician from the Department of Clinical Laboratory), Liu Song (assistant researcher of the Bioinformatics Platform, Clinical Medical Institute), and Dr. Wang Xu (Department of Rheumatology) are co-first authors.
Written by and pictures courtesy of the Department of Clinical Laboratory
Edited by Wang Jingxia
Chief Editor Duan Wenli
Supervised by Wu Peixin
