On October 16, 2025, the
rheumatology team led by Chief Physician Zhang Fengchun at PUMCH published the
phase 3 clinical trial results of telitacicept—a novel biological agent
independently developed in China—in the internationally authoritative The
New England Journal of Medicine (NEJM, IF: 78.5). The study
demonstrated the efficacy and safety of telitacicept in Chinese patients with
systemic lupus erythematosus (SLE), providing important clinical evidence for
its use in combination therapy for SLE. Telitacicept is expected to offer a new
treatment option for SLE and other autoimmune diseases in which humoral
immunity plays a significant role. This represents an important contribution by
the Chinese medical community to SLE patients worldwide.

SLE
predominantly affects women of childbearing age and commonly involves multiple
organs and systems. The disease is chronic, prone to relapse, and difficult to
cure. Currently, treatment options with approved indications are very limited.
Even after treatment with existing regimens, some patients still experience
adverse outcomes such as poor disease control, target organ damage, and various
complications, which severely impact their quality of life and even lifespan.
B
lymphocytes are the primary source of autoantibodies and important
antigen-presenting cells, playing a crucial role in the pathogenesis of SLE.
B-lymphocyte stimulator (BLyS) and a proliferation-inducing ligand (APRIL) are
important factors in the differentiation, survival, maturation, and antibody
secretion processes of B lymphocytes. Telitacicept is a biological agent
independently developed in China that targets B lymphocytes by simultaneously
binding to both BLyS and APRIL, thereby blocking B lymphocyte maturation.
This
study was a phase 3, multicenter, double-blind, randomized, placebo-controlled
clinical trial that enrolled 335 adult SLE patients with moderate or higher
disease activity despite standard therapy from 42 research centers. Patients
were randomly assigned in a 1:1 ratio to receive either telitacicept (160 mg)
or placebo by subcutaneous injection, in addition to standard therapy.
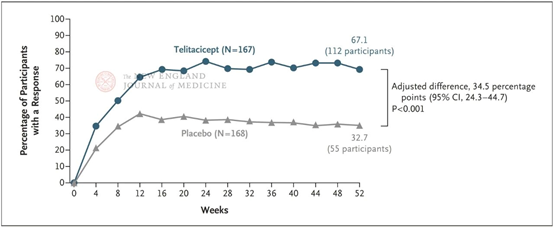
▲ Study data
Results showed that at week 52, the response rates on the modified SRI-4 were 67.1% in the telitacicept group and 32.7% in the placebo group, with a significant difference between the two (P<0.001). Moreover, from week 4 through the end of the 52-week follow-up period, the response rate on SRI-4 in the telitacicept group was consistently higher than in the placebo group, demonstrating the stability of telitacicept's therapeutic advantage.
Safety assessment showed that adverse events primarily included infections (upper respiratory tract infection: 31.7% in the telitacicept group vs. 19.0% in the placebo group), a reduced immunoglobulin level (15.6% in the telitacicept group vs. 1.2% in the placebo group), and injection-site reactions (12.6% in the telitacicept group vs. 0.6% in the placebo group), similar to other marketed B lymphocyte-targeted biological agents and subcutaneously administered drugs. Regarding the incidence of serious adverse events, particularly trial-related ones, the telitacicept group was not higher than the placebo group, demonstrating acceptable safety.
Under the leadership and guidance of Chief Physician Zhang Fengchun, the phase 1, 2a, 2b, and 3 clinical trials of this drug were completed over more than ten years.
Chief Physician Wang Li from the Department of Rheumatology at PUMCH is the first author, and Chief Physician Zhang Fengchun is the corresponding author. Professor Ronald van Vollenhoven from Amsterdam University Medical Center is both first and corresponding author. Professor Fang Jianmin from Tongji University is a corresponding author.
Written
by and pictures courtesy of the Department of Rheumatology
Edited
by Fu Tanping and Chen Xiao
Chief
editor Duan Wenli
Supervised by Wu Peixin
