Recently, Professor Chen Jie’s team from the Department of Pathology, PUMCH published a paper in “Modern Pathology” (a tier 1 journal, or among the top 5%, as ranked by the Chinese Academy of Sciences). The team analyzed the immune microenvironment of 136 cases of intraductal papillary mucinous neoplasm (IPMN) of the pancreas. By examining the changes in important cells and molecules, they revealed the histologic subtype heterogeneity of the immune characteristics of this type of tumor, providing new evidence for early prevention and treatment strategies for pancreatic cancer. This research was supported by the National High Level Hospital Clinical Research Funding.

Pancreatic ductal adenocarcinoma is the most common type of pancreatic cancer and has three common precursor lesions, namely intraductal papillary mucinous neoplasm (IPMN), pancreatic intraepithelial neoplasia (PanIN), and mucinous cystic neoplasm. IPMN can be detected early through imaging examinations, providing more possibilities for improving the prognosis of such pancreatic cancer patients. Currently, immune therapy strategies targeting PD-1/PD-L1 to block tumor immune escape and eliminate tumor cells have been successfully applied in treating many cancers. In preclinical studies of various tumors, the VISTA (V-domain immunoglobulin suppressor of T-cell activation) blockade therapy has also demonstrated applicability potential. Previous studies have found that the efficacy of tumor immunotherapy is heavily influenced by the tumor immune microenvironment, in which CD8+ T cells are important immune cells that play a role in killing tumor when PD-1/PD-L1 are targeted, while CD68+ macrophages inhibit anti-tumor immunity. However, the academic community has not worked out the characteristics of immune microenvironmental changes during the progression from IPMN to pancreatic cancer. Therefore, the prospects for applying immunotherapy to the treatment of IPMN-related pancreatic cancer are not clear yet.
The study investigated CD8+ T cells, CD68+ macrophages, PD-L1, and VISTA in 60 patients with IPMN with associated invasive carcinoma using immunohistochemistry, visually demonstrating the dynamic changes of important immune cells and molecules in the immune microenvironment during the malignant changes of IPMN. They were compared against those in 76 patients with IPMN without invasive carcinoma.
The research findings revealed that during the progression of IPMN to invasive carcinoma, a decrease in CD8+ T cells and an increase in CD68+ macrophages were observed. A multivariate analysis revealed that a higher degreeenrichment of CD68+ macrophage infiltration was an important factor indicating poor prognosis in patients with IPMN associated with invasive carcinoma. These findings also provide new insights for pathologists in better identifying IPMN-related invasive carcinoma.
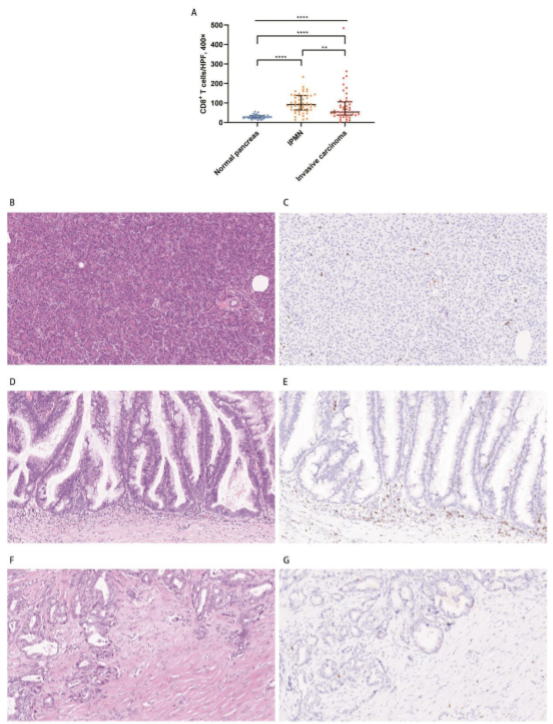
▲Significantly reduced CD8+ T cell infiltration in patients with IPMN associated with invasive carcinoma
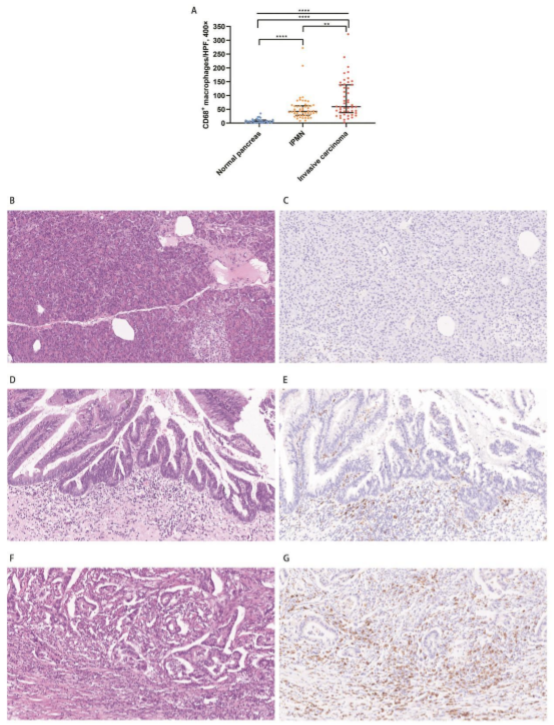
▲A higher abundance Enrichment of CD68+ macrophages in patients with IPMN associated with invasive carcinoma
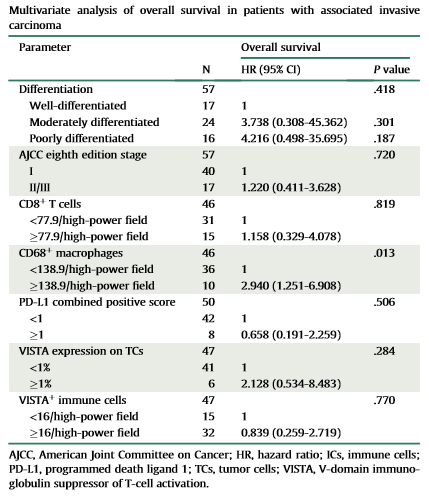
▲Multivariate analysis of overall survival in patients with IPMN associated with invasive carcinoma
The research findings also revealed that PD-L1 positivity was visibly observed in gastric-type/pancreatobiliary-type IPMN with associated invasive carcinoma, while accumulation of VISTA+ immune cells was predominantly observed in the intestinal-type IPMN. This suggests significant heterogeneity in the histological -subtypes subtype specificity of immune characteristicssignature in IPMN, shedding new light on the pathological diagnosis of and the development of prevention and treatment strategies for IPMN.
Written by Gan Dingzhu and Mo Shengwei
Edited by Gan Dingzhu and Chen Xiao
Translated by Liu Haiyan
Reviewed by Lu Junliang and Wang Yao
